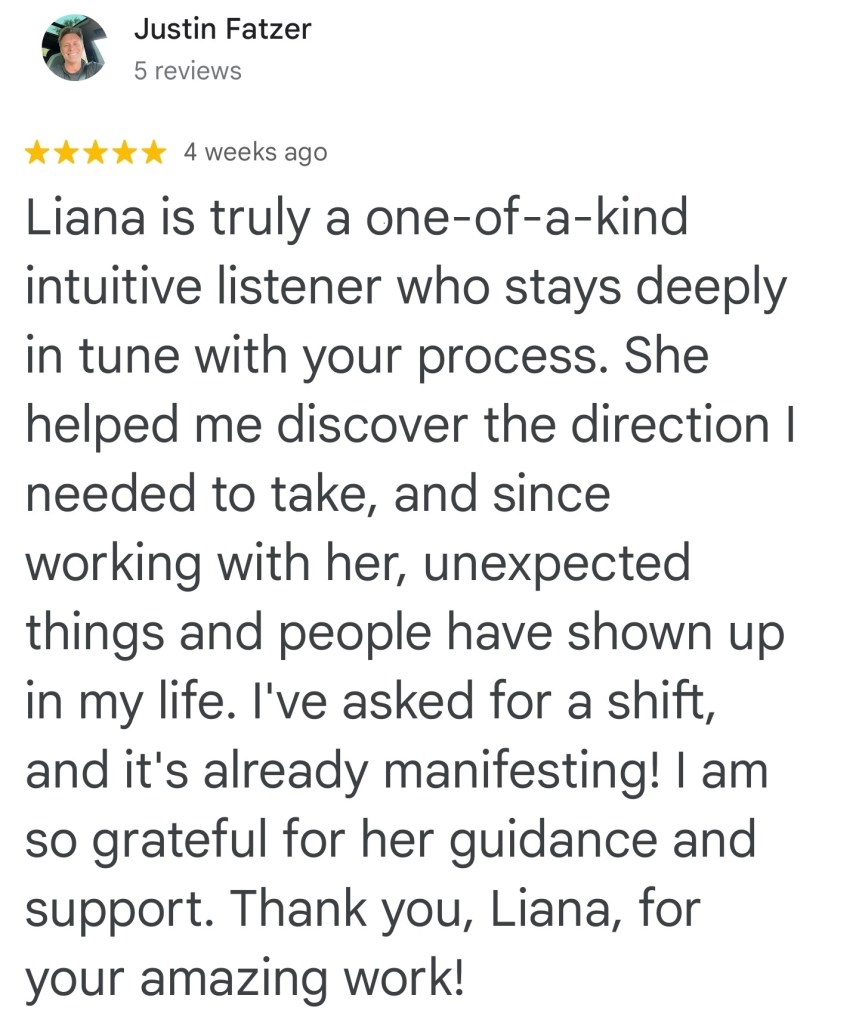
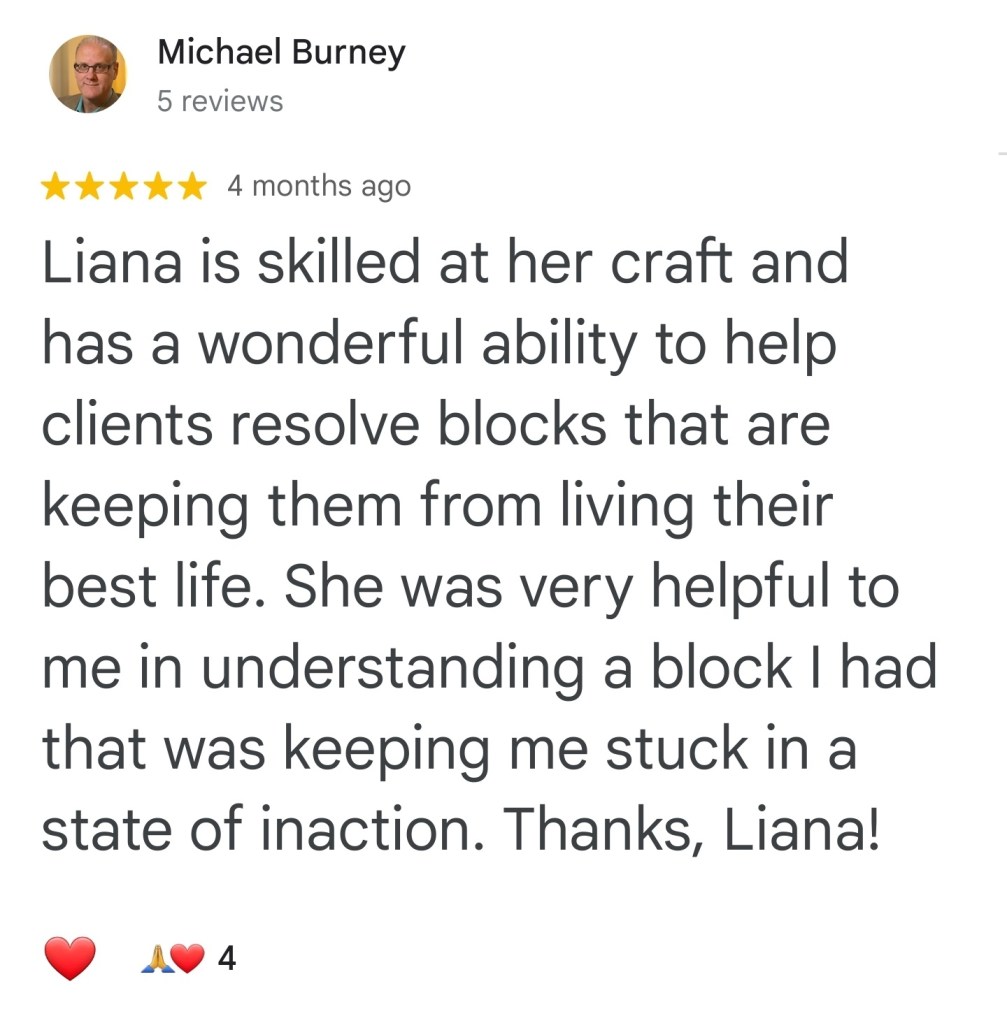
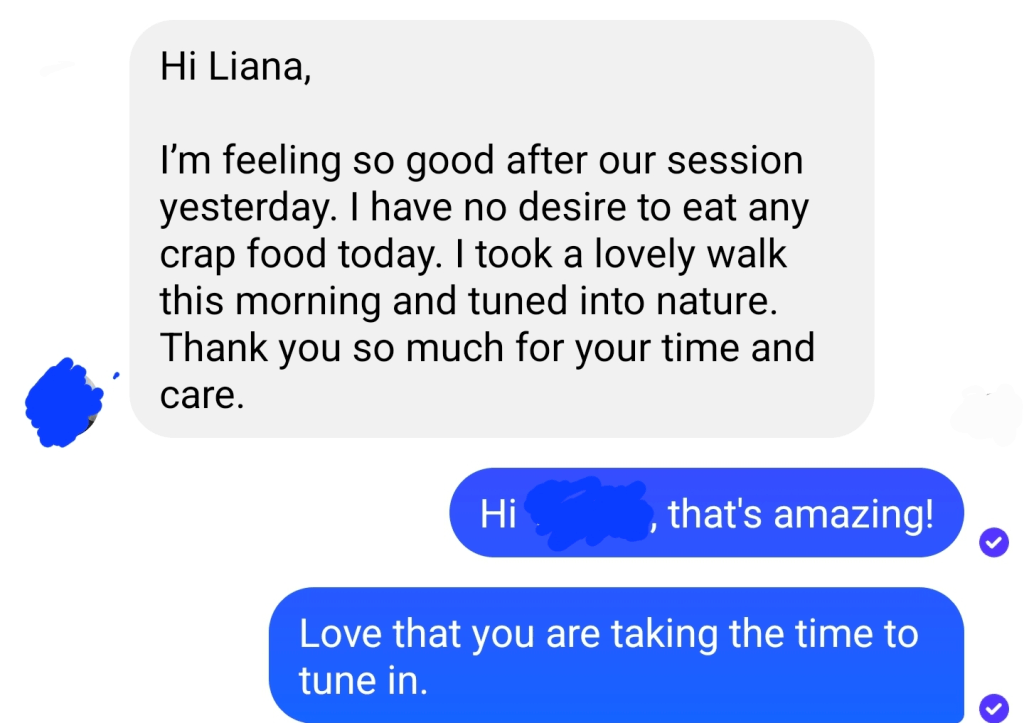
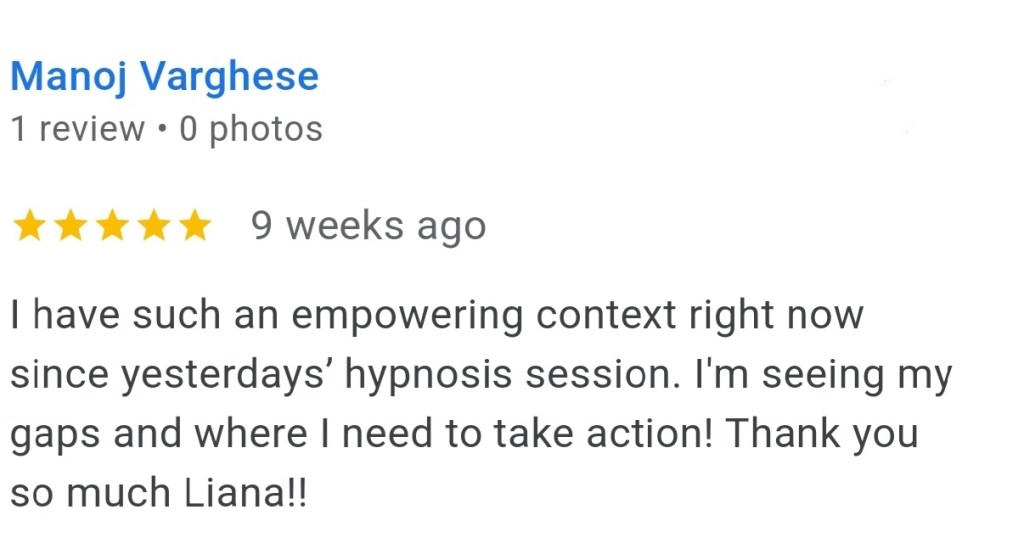
Can hypnosis change your brain activity? EEG research says yes.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a powerful tool used to measure the brain’s electrical activity. When applied to hypnosis, EEG studies reveal something fascinating: hypnosis isn’t just deep relaxation—it creates a distinct and measurable shift in brainwave patterns.
What Happens in the Brain During Hypnosis?
During hypnosis, the brain shows:
🔹 Increased Theta and Alpha Brainwaves
- Theta waves (4–8 Hz): Linked to deep meditation, creativity, and subconscious processing.
- Alpha waves (8–13 Hz): Associated with calm focus, light trance, and internal attention.
Together, these waves signal a deeply relaxed, inward-focused state—similar to meditation or the edge of sleep—ideal for therapeutic suggestion and imagination.
🔹 Decreased Beta and Gamma Brainwaves
- Beta waves (13–30 Hz): Responsible for logical thinking, active problem-solving, and conscious control.
- Gamma waves (30–100+ Hz): Related to high-level cognition and awareness.
When these faster waves are suppressed, the brain quiets its inner critic and becomes more open to positive possibilities. This supports hypnosis for anxiety relief, behavioral change, and trauma recovery.
Brain Connectivity During Hypnosis: New Insights from 2024 EEG Research
A 2024 study published in Cortex discovered:
Increased frontoparietal connectivity – signaling enhanced coordination between the frontal lobe (decision-making and attention) and parietal lobe (sensory integration and spatial awareness).
Suppressed beta and gamma activity, pointing to less cognitive resistance and more subconscious access.
These findings suggest the hypnotized brain is uniquely wired for transformation, not just relaxation.
Synchronization of Brain Hemispheres
EEG studies also show that hypnosis boosts communication between the left hemisphere (logical, analytical thinking) and right hemisphere (intuition, creativity). This cross-brain collaboration enhances mental flexibility, allowing individuals to respond more openly to possibilities created in hypnosis.
Practical Applications of Hypnosis Research
Advances in brain scanning technology have made it possible to measure hypnosis, boosting its credibility and use across multiple fields, such as:
Behavioral Change
- Smoking addiction—cuts out hidden triggers and boosts the drive to quit
- Overeating and emotional eating—helps with portion sizes, curbs cravings, and improves body image
- Alcohol and drug dependency—supports recovery and prevents relapse as a complementary tool
- Compulsive habits—tackles nail-biting, hair pulling (trichotillomania), and skin picking
- Chronic procrastination and self-sabotage—breaks patterns that block goals
- Unhealthy sleep habits—addresses night eating, bedtime struggles, and erratic schedules
- Fear-driven avoidance—eases irrational fears, like skipping doctor visits or social gatherings
Performance Enhancement
- Performance anxiety—calms nerves for athletes, musicians, speakers, and test-takers
- Fear of failure or success—eases doubts that spark avoidance or self-sabotage
- Mental blocks in learning—lifts math anxiety, test panic, or reading struggles
- Low self-confidence and imposter syndrome—boosts belief for career growth or creativity
- Stress and burnout—relieves pressure in intense jobs or competitive settings
- Distractions and scattered focus—sharpens concentration and keeps you in the moment
How Can Hypnosis Help You?
EEG research confirms that hypnosis creates a unique brain state—not just relaxation. It increases alpha and theta waves for deep focus and calm, reduces beta and gamma waves linked to critical thinking, and enhances connectivity across brain regions and hemispheres.
These measurable brain shifts explain why hypnosis is so effective for healing, behavioral change, and subconscious transformation.
Let’s connect!
Pure Possibilities
Change Your Mind.
Change Your Life.














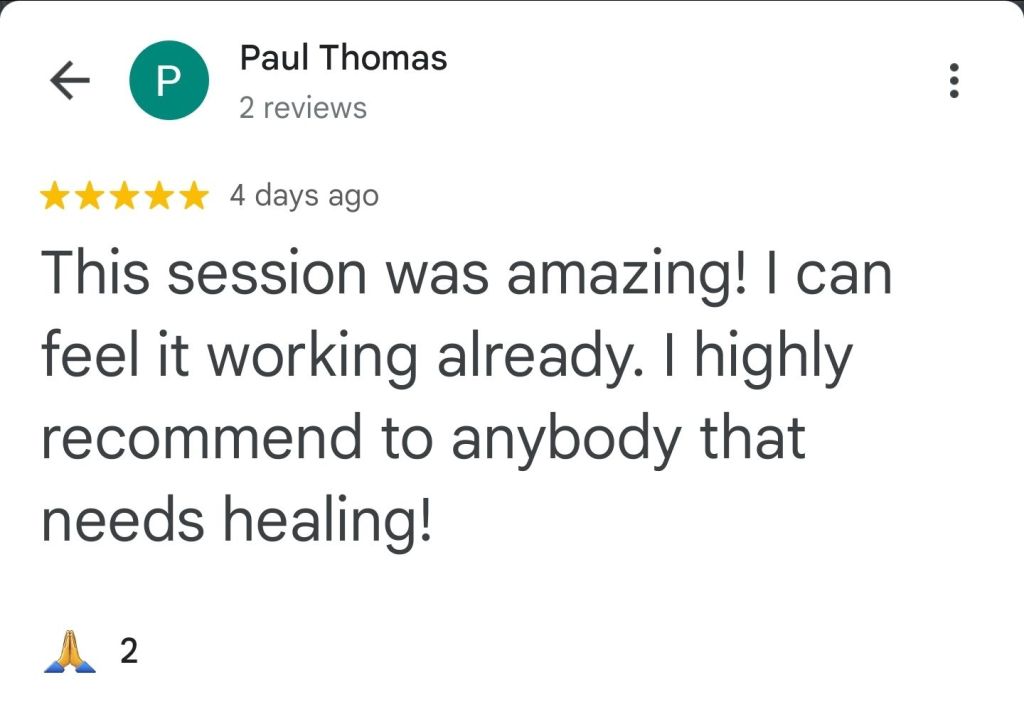

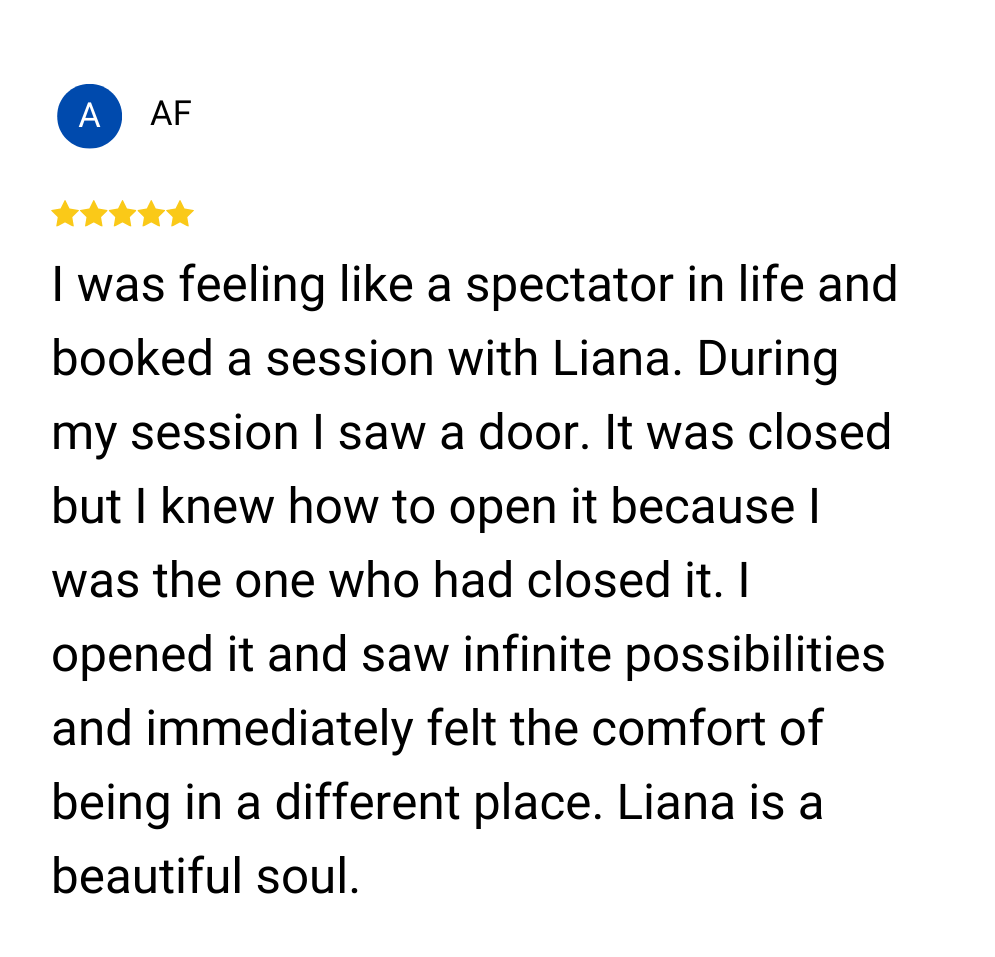







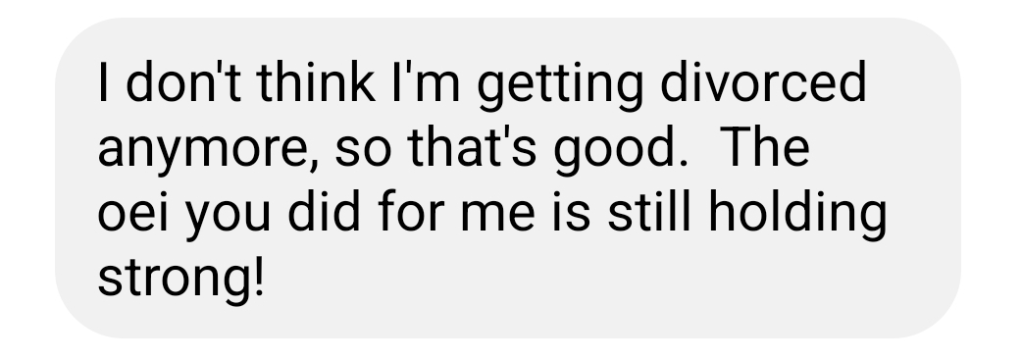

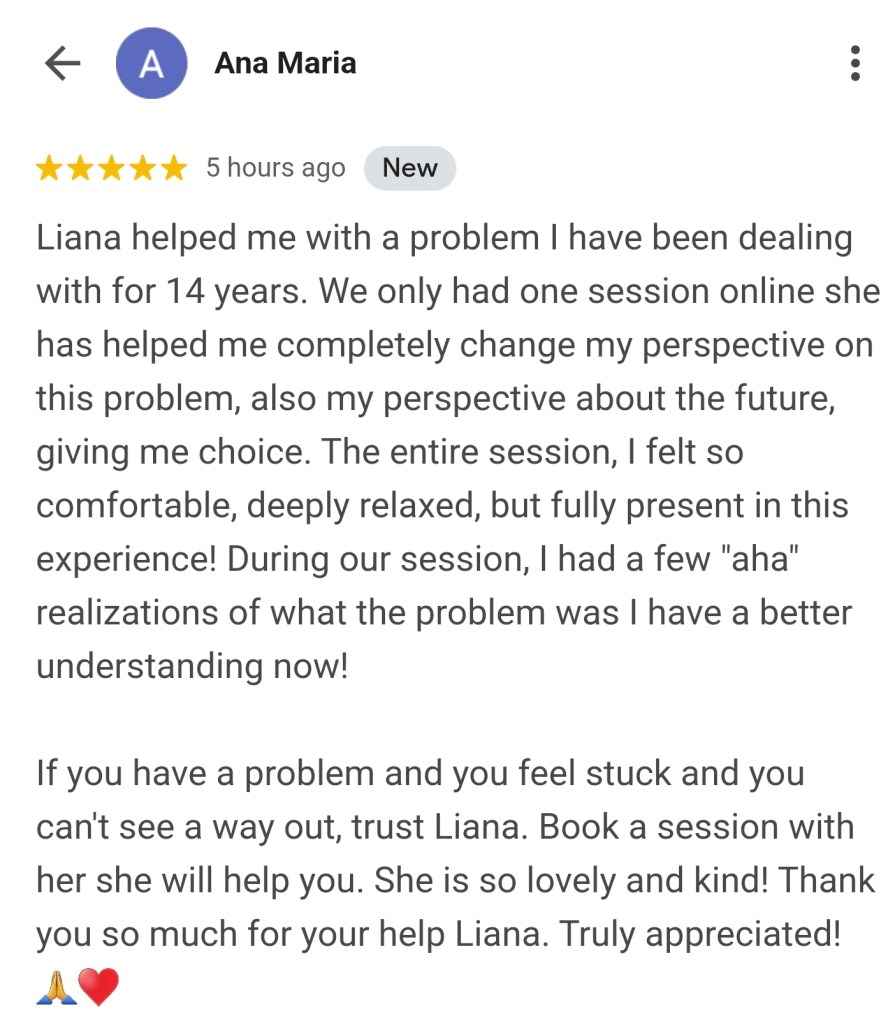

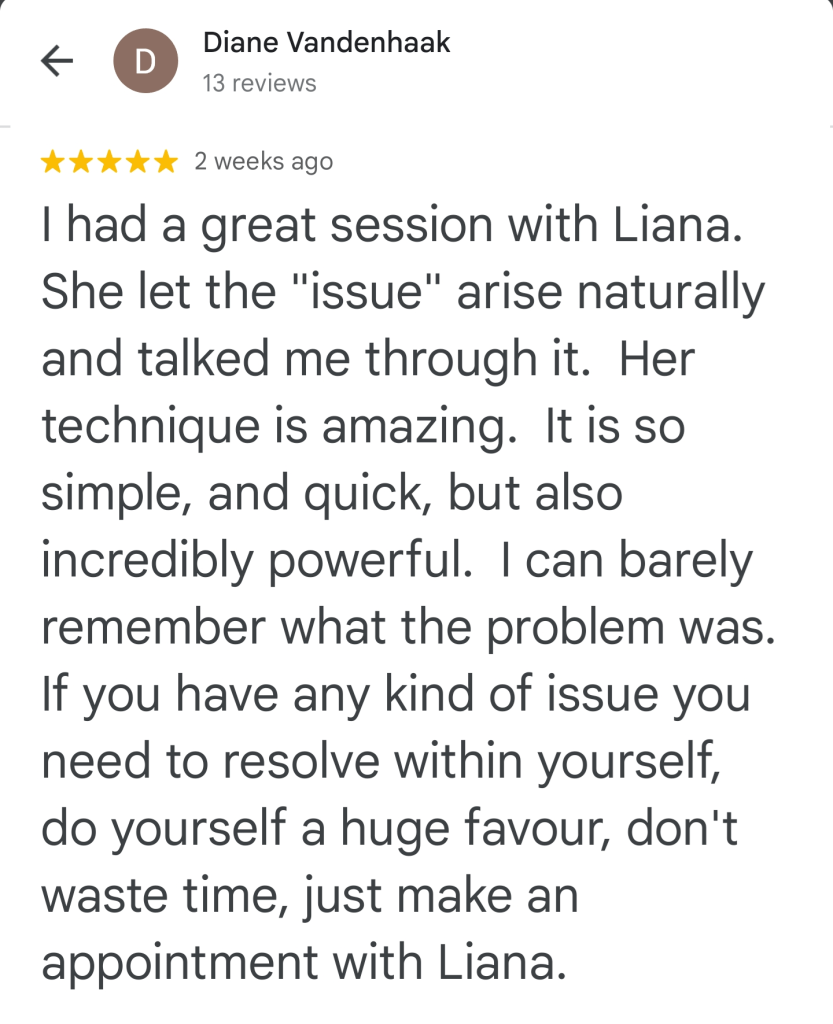





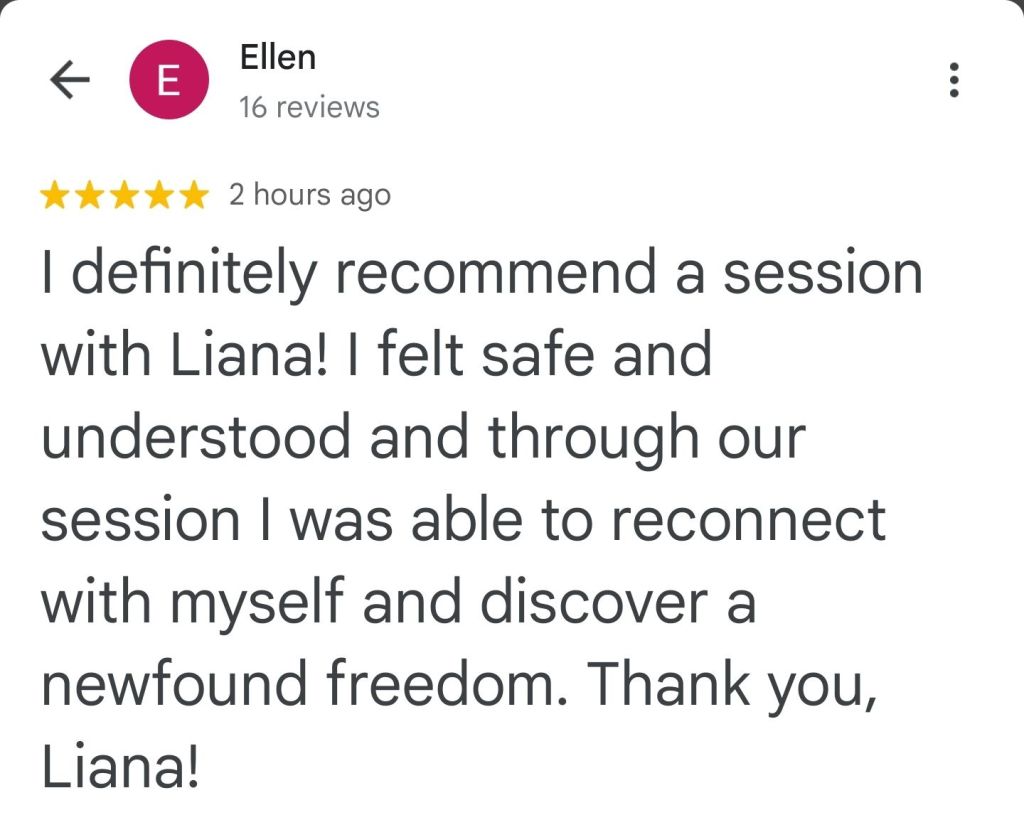

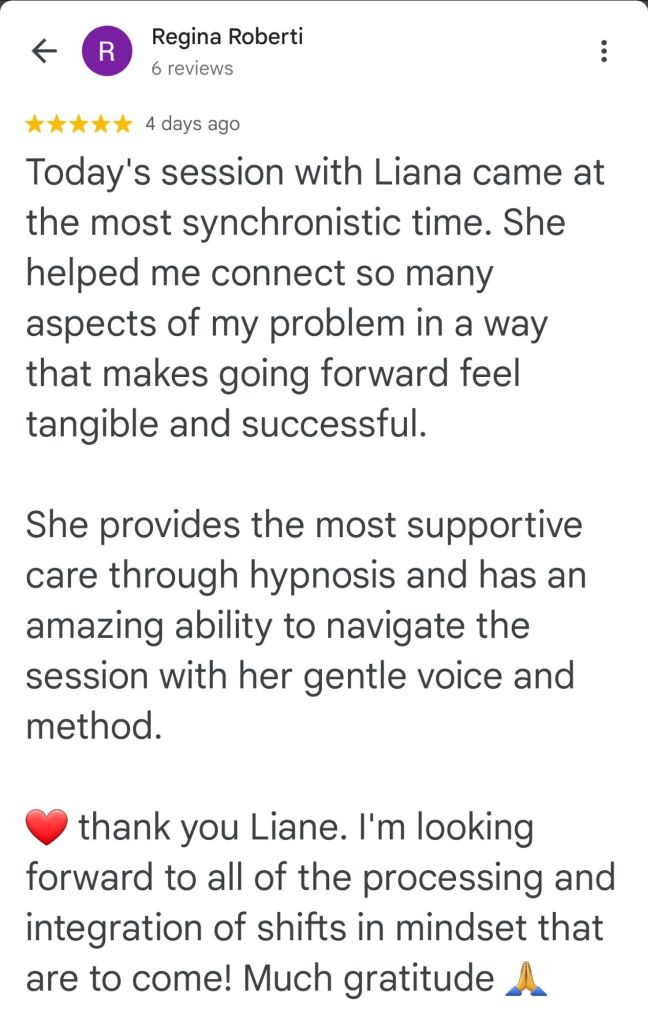






Leave a comment